Introduction
oncoanalyser by default assigns compute resource labels
to each process which are defined in conf/base.config (as is standard in nf-core pipelines).
For example, process_high is defined as:
process {
withLabel: process_high {
cpus = { 12 * task.attempt }
memory = { 72.GB * task.attempt }
time = { 16.h * task.attempt }
}
}The labels used by each process can be grabbed with this command:
grep -r "label 'process_" modules/*/ | sort
modules/local/amber/main.nf: label 'process_high'
modules/local/bamtools/main.nf: label 'process_medium'
modules/local/bwa-mem2/mem/main.nf: label 'process_high'
...Recommended settings per process
Hartwig Medical Foundation uses more granular compute resources settings when running oncoanalyser in Google Cloud.
The settings below are used for both whole genome and panel sequencing runs. Regular expressions are provided to the
withName directive to target multiple processes. Disk space is specified when a process has large files
(BAM or FASTQ files) as input or output.
process {
withName: 'FASTP' { memory = 72.GB; cpus = 12; disk = 375.GB }
withName: '.*ALIGN' { memory = 72.GB; cpus = 12; disk = 750.GB }
withName: 'AMBER' { memory = 24.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'BAMTOOLS' { memory = 24.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'CHORD' { memory = 12.GB; cpus = 4 }
withName: 'CIDER' { memory = 24.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'COBALT' { memory = 24.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'CUPPA' { memory = 16.GB; cpus = 4 }
withName: 'ESVEE' { memory = 96.GB; cpus = 32; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'ISOFOX' { memory = 24.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'LILAC' { memory = 64.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'LINX_.*' { memory = 16.GB; cpus = 8 }
withName: 'ORANGE' { memory = 16.GB; cpus = 4 }
withName: 'PAVE.*' { memory = 32.GB; cpus = 8 }
withName: 'PEACH' { memory = 4.GB ; cpus = 2 }
withName: 'PURPLE' { memory = 40.GB; cpus = 8 }
withName: 'REDUX' { memory = 72.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 750.GB }
withName: 'SAGE.*' { memory = 72.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'TEAL_PREP' { memory = 72.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'TEAL_PIPELINE' { memory = 32.GB; cpus = 8 ; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'VIRUSBREAKEND' { memory = 64.GB; cpus = 16; disk = 375.GB }
withName: 'VIRUSINTERPRETER' { memory = 8.GB ; cpus = 2 }
withName: 'WISP' { memory = 16.GB; cpus = 4 ; disk = 375.GB }
}You can use the above config as a starting point for tuning the compute resources for your own runs. For high depth panel samples for example, you may need to increase the memory for alignment, read processing (REDUX), and/or small variant calling (SAGE) steps.
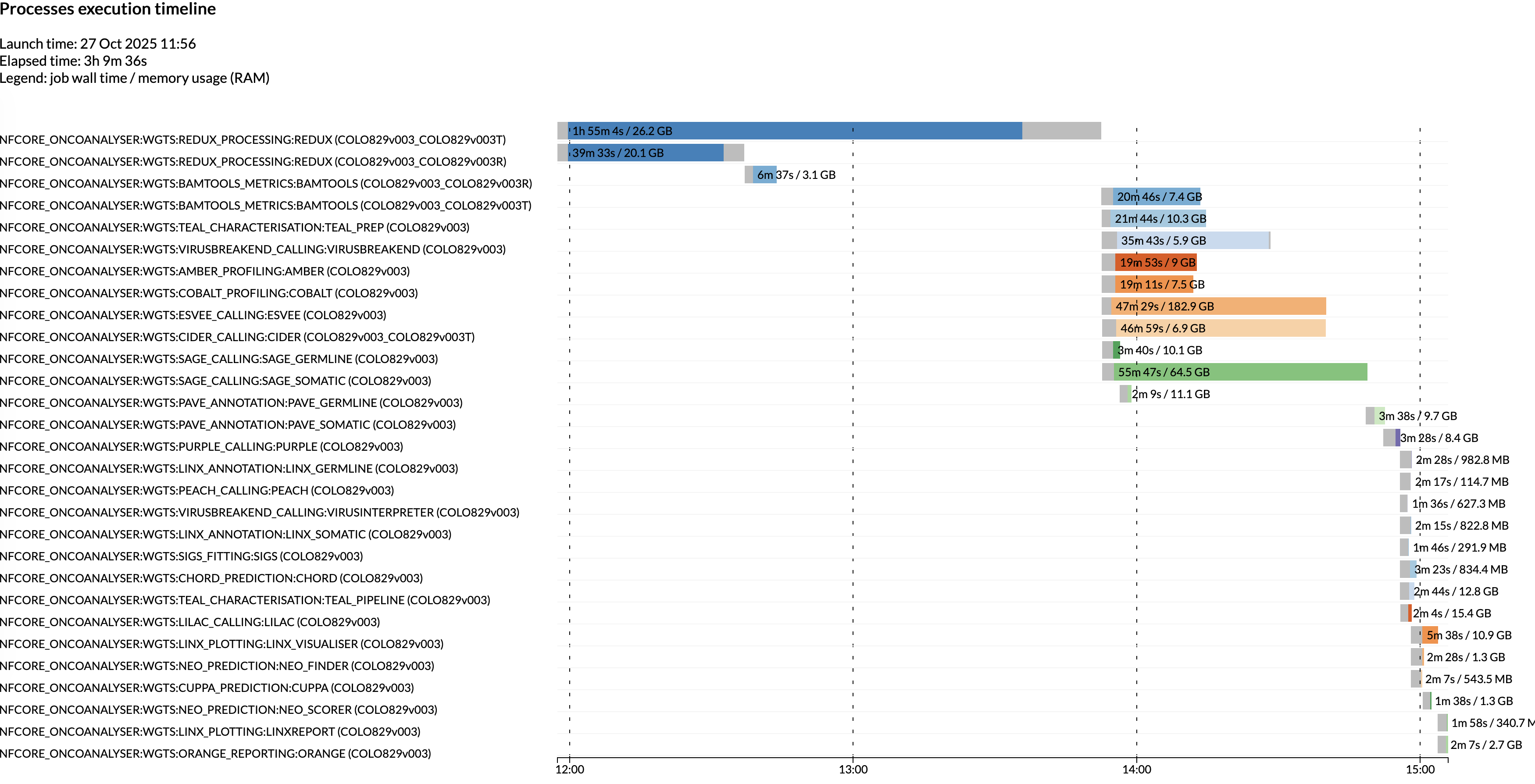
Pipeline performance
The below Nextflow execution timeline shows the runtime and memory usage per process when oncoanalyser is run with:
- Paired 100x tumor / 30x normal WGS samples
- Starting from BAMs
- Parallel job execution via Google batch
- The above recommended settings per process.
Note that your runtime will vary depending on several factors such as sequencing depth, number of small/structural variants, or parallel vs. non-parallel job execution.
Max resources
When running multiple samples in one oncoanalyser run, we recommend setting the
maximum resources that oncoanalyser is allowed to use.
This is to prevent the compounding requested compute resources exceeding the available resources on a machine or
allowed by your job scheduler. An example config could look like:
process {
resourceLimits = [
cpus: 64,
memory: 120.GB, // Provides leeway on a 128.GB machine
disk: 1500.GB,
time: 48.h
]
}Automatically retry with increased compute resources
You may consider automatically increasing the compute resources upon processes failing, e.g. due to out-of-memory errors. This can be achieved using errorStrategy and maxRetries
In the below example config, we increase the memory for REDUX by 64GB for each attempt.
process {
// Currently, all of WiGiTS tools return a exit code of 1 on failure.
// We only want to retry for other exit codes which relate to Nextflow or the environment (e.g. out of memory error).
errorStrategy = { task.exitStatus != 1 ? 'retry' : 'finish' }
maxRetries = 3
withName: REDUX {
memory = check_max( 64.GB * task.attempt, 'memory' )
}
}